Prerequisites for Active/Passive HA
To set up high availability on your Palo Alto Networks firewalls, you need a pair of firewalls that meet the following requirements:
- The same model—Both the firewalls in the pair must be of the same hardware model or virtual machine model.
- The same PAN-OS version—Both the firewalls should be running the same PAN-OS version and must each be up-to-date on the application, URL, and threat databases.
- The same multi virtual system capability—Both firewalls must have Multi Virtual System Capability either enabled or not enabled. When enabled, each firewall requires its own multiple virtual systems licenses.
- The same type of interfaces—Dedicated HA links, or a combination of the management port and in-band ports that are set to interface type HA.
- Determine the IP address for the HA1 (control) connection between the HA peers. The HA1 IP address for both peers must be on the same subnet if they are directly connected or are connected to the same switch.For firewalls without dedicated HA ports, you can use the management port for the control connection. Using the management port provides a direct communication link between the management planes on both firewalls. However, because the management ports will not be directly cabled between the peers, make sure that you have a route that connects these two interfaces across your network.
- If you use Layer 3 as the transport method for the HA2 (data) connection, determine the IP address for the HA2 link. Use Layer 3 only if the HA2 connection must communicate over a routed network. The IP subnet for the HA2 links must not overlap with that of the HA1 links or with any other subnet assigned to the data ports on the firewall.
- The same set of licenses—Licenses are unique to each firewall and cannot be shared between the firewalls. Therefore, you must license both firewalls identically. If both firewalls do not have an identical set of licenses, they cannot synchronize configuration information and maintain parity for a seamless failover.
Overview
Steps
Configuration
High Availability
Management
Overview
Steps
Additional info
Configure Active/Passive HA
CONFIGURATION OF PALO ALTO ACTIVE TO PASSIVE
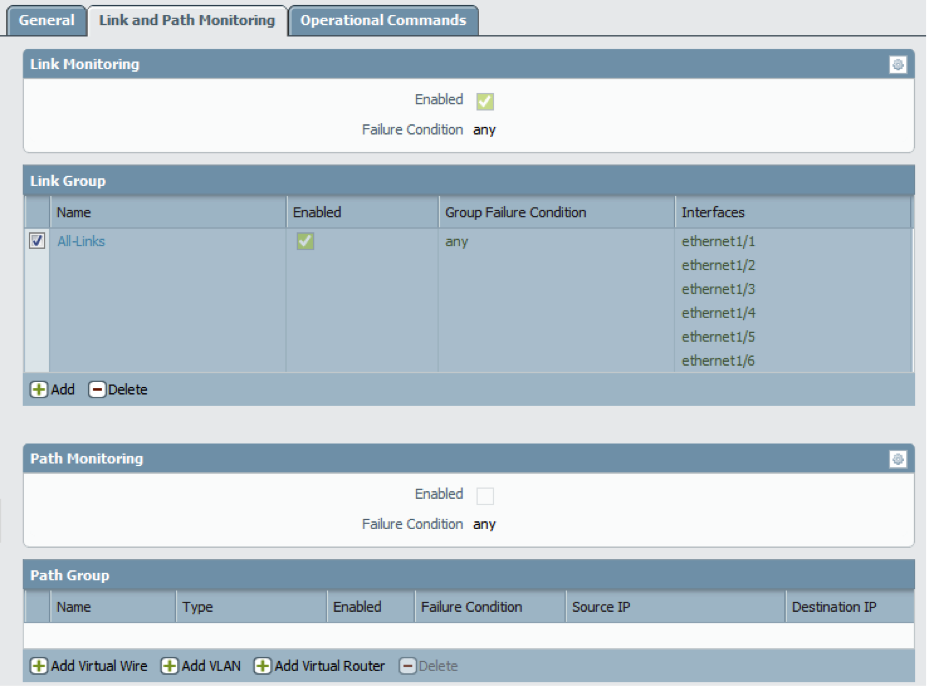
Define HA Failover Conditions
Verify Failover
Configure Active/Active HA PALO ALTO
Configure Active/Active HA
The following procedure describes the basic workflow for configuring your firewalls in an active/active configuration. However, before you begin, Determine Your Active/Active Use Case for configuration examples more tailored to your specific network environment.
To configure active/active, first complete the following steps on one peer and then complete them on the second peer, ensuring that you set the Device ID to different values (0 or 1) on each peer.
- Connect the HA ports to set up a physical connection between the firewalls.For each use case, the firewalls could be any hardware model; choose the HA3 step that corresponds with your model.
- For firewalls with dedicated HA ports, use an Ethernet cable to connect the dedicated HA1 ports and the HA2 ports on peers. Use a crossover cable if the peers are directly connected to each other.
- For firewalls without dedicated HA ports, select two data interfaces for the HA2 link and the backup HA1 link. Then, use an Ethernet cable to connect these in-band HA interfaces across both firewalls. Use the management port for the HA1 link and ensure that the management ports can connect to each other across your network.
- For HA3:
- On PA-7000 Series firewalls, connect the High Speed Chassis Interconnect (HSCI-A) on the first chassis to the HSCI-A on the second chassis, and the HSCI-B on the first chassis to the HSCI-B on the second chassis. On a PA-5200 Series firewall (which has one HSCI port), connect the HSCI port on the first chassis to the HSCI port on the second chassis. You can also use data ports for HA3 on PA-5200 Series firewalls.
- On any other hardware model, use dataplane interfaces for HA3.
- Enable ping on the management port.Enabling ping allows the management port to exchange heartbeat backup information.
- In , edit Management Interface Settings.
- Select Ping as a service that is permitted on the interface.
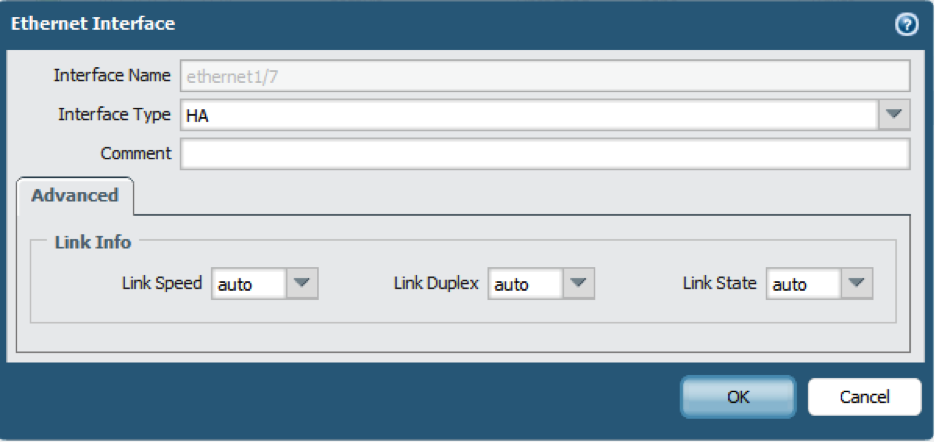
- If the firewall does not have dedicated HA ports, set up the data ports to function as HA ports.For firewalls with dedicated HA ports continue to the next step.
- Select .
- Confirm that the link is up on the ports that you want to use.
- Select the interface and set Interface Type to HA.
- Set the Link Speed and Link Duplex settings, as appropriate.
- Enable active/active HA and set the group ID.
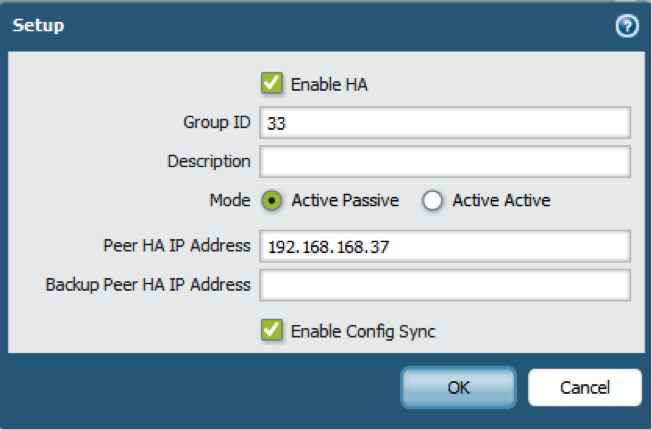
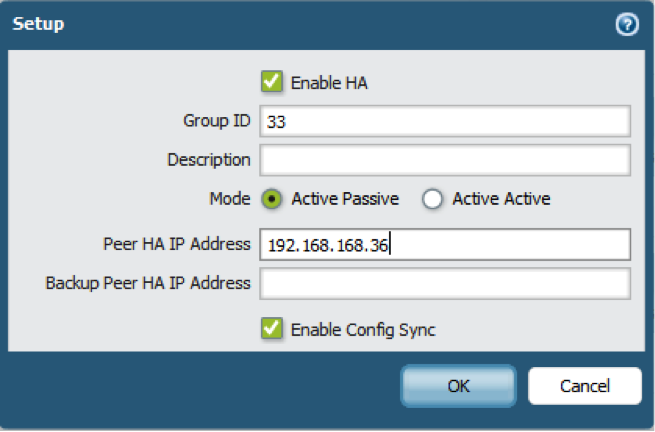
- In , edit Setup.
- Select Enable HA.
- Enter a Group ID, which must be the same for both firewalls. The firewall uses the Group ID to calculate the virtual MAC address (range is 1-63).
- (Optional) Enter a Description.
- For Mode, select Active Active.
- Set the Device ID, enable synchronization, and identify the control link on the peer firewall
- In , edit Setup.
- Select Device ID as follows:
- When configuring the first peer, set the Device ID to 0.
- When configuring the second peer, set the Device ID to 1.
- Select Enable Config Sync. This setting is required to synchronize the two firewall configurations (enabled by default).
- Enter the Peer HA1 IP Address, which is the IP address of the HA1 control link on the peer firewall.
- (Optional) Enter a Backup Peer HA1 IP Address, which is the IP address of the backup control link on the peer firewall.
- Click OK.
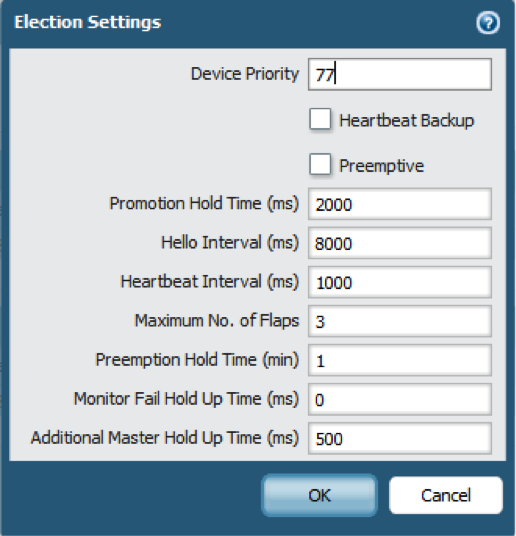
- Determine whether or not the firewall with the lower Device ID preempts the active-primary firewall upon recovery from a failure.
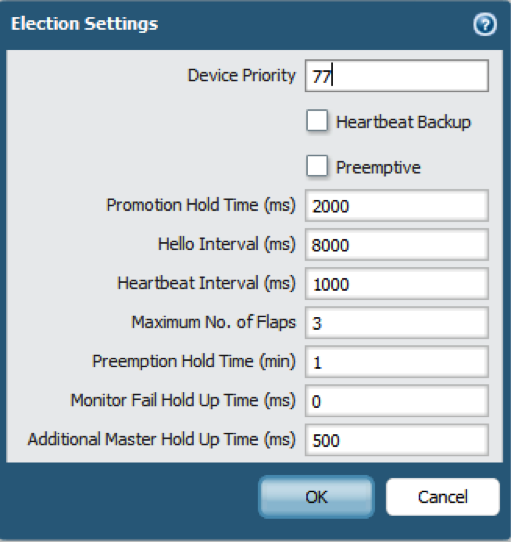
- In , edit Election Settings.
- Select Preemptive to cause the firewall with the lower Device ID to automatically resume active-primary operation after either firewall recovers from a failure. Both firewalls must have Preemptive selected for preemption to occur.Leave Preemptive unselected if you want the active-primary role to remain with the current firewall until you manually make the recovered firewall the active-primary firewall.
- Enable heartbeat backup if your control link uses a dedicated HA port or an in-band port.You need not enable heartbeat backup if you are using the management port for the control link.
- In , edit Election Settings.
- Select Heartbeat Backup.To allow the heartbeats to be transmitted between the firewalls, you must verify that the management port across both peers can route to each other.Enabling heartbeat backup allows you to prevent a split-brain situation. Split brain occurs when the HA1 link goes down, causing the firewall to miss heartbeats, although the firewall is still functioning. In such a situation, each peer believes the other is down and attempts to start services that are running, thereby causing a split brain. Enabling heartbeat backup prevents split brain because redundant heartbeats and hello messages are transmitted over the management port.
- (Optional) Modify the HA Timers .By default, the HA timer profile is set to the Recommended profile and is suited for most HA deployments.
- In , edit Election Settings.
- Select Aggressive to trigger faster failover. Select Advanced to define custom values for triggering failover in your setup.To view the preset value for an individual timer included in a profile, select Advanced and click Load Recommended or Load Aggressive. The preset values for your hardware model will be displayed on screen.
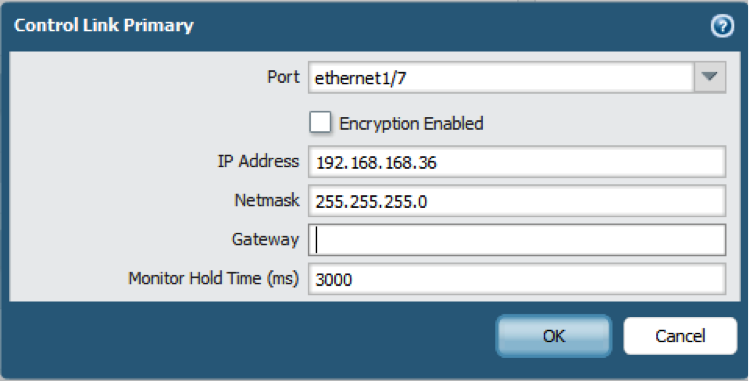
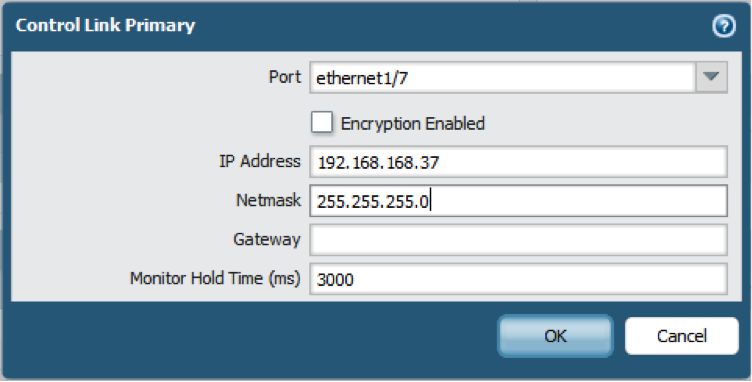
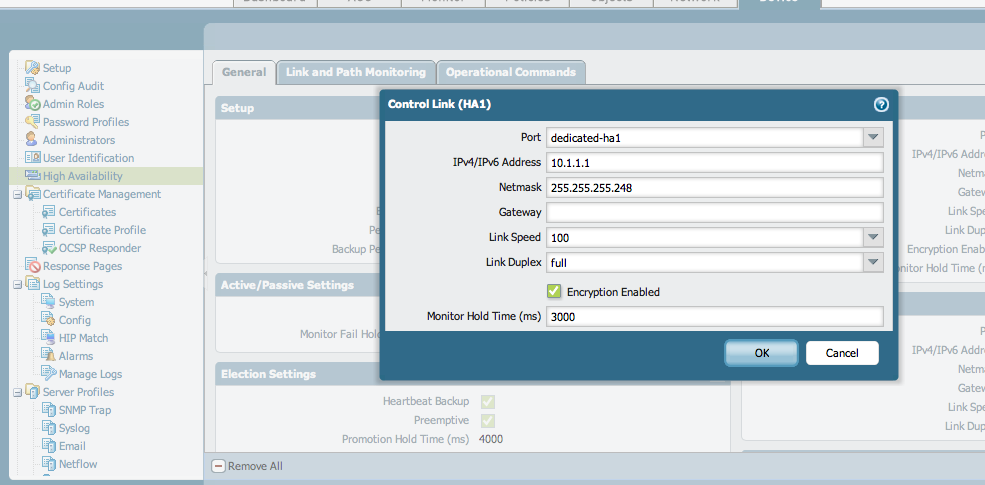
- Set up the control link connection.This example uses an in-band port that is set to interface type HA.For firewalls that use the management port as the control link, the IP address information is automatically pre-populated.
- In , edit Control Link (HA1).
- Select the Port that you have cabled for use as the HA1 link.
- Set the IPv4/IPv6 Address and Netmask.If the HA1 interfaces are on separate subnets, enter the IP address of the Gateway. Do not add a gateway address if the firewalls are directly connected.
- (Optional) Enable encryption for the control link connection.This is typically used to secure the link if the two firewalls are not directly connected, that is if the ports are connected to a switch or a router.
- Export the HA key from one firewall and import it into the peer firewall.
- Select .
- Select Export HA key. Save the HA key to a network location that the peer can access.
- On the peer firewall, select , and select Import HA key to browse to the location that you saved the key and import it in to the peer.
- In , edit the Control Link (HA1).
- Select Encryption Enabled.
- Export the HA key from one firewall and import it into the peer firewall.
- Set up the backup control link connection.
- In , edit Control Link (HA1 Backup).
- Select the HA1 backup interface and set the IPv4/IPv6 Address and Netmask.
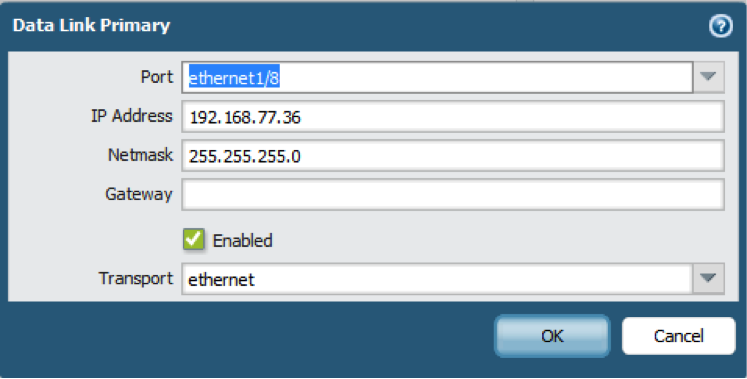
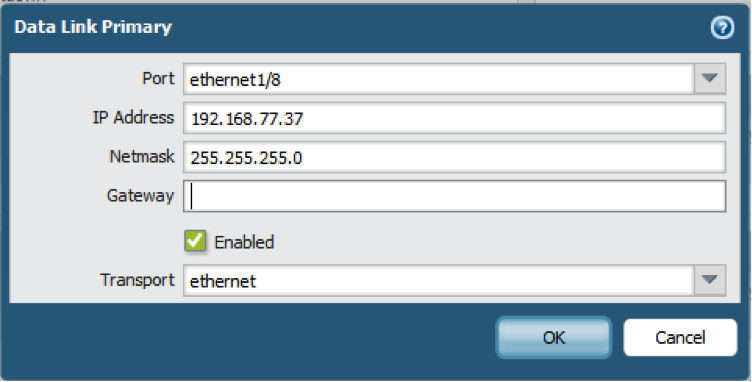
- Set up the data link connection (HA2) and the backup HA2 connection between the firewalls.
- In , edit Data Link (HA2).
- Select the Port to use for the data link connection.
- Select the Transport method. The default is ethernet, and will work when the HA pair is connected directly or through a switch. If you need to route the data link traffic through the network, select IP or UDP as the transport mode.
- If you use IP or UDP as the transport method, enter the IPv4/IPv6 Address and Netmask.
- Verify that Enable Session Synchronization is selected.
- Select HA2 Keep-alive to enable monitoring on the HA2 data link between the HA peers. If a failure occurs based on the threshold that is set (default is 10000 ms), the defined action will occur. For active/passive configuration, a critical system log message is generated when an HA2 keep-alive failure occurs.You can configure the HA2 keep-alive option on both firewalls, or just one firewall in the HA pair. If the option is only enabled on one firewall, only that firewall will send the keep-alive messages. The other firewall will be notified if a failure occurs.
- Edit the Data Link (HA2 Backup) section, select the interface, and add the IPv4/IPv6 Addressand Netmask.
- Click OK.
- Configure the HA3 link for packet forwarding.
- In , edit Packet Forwarding.
- For HA3 Interface, select the interface you want to use to forward packets between active/active HA peers. It must be a dedicated interface capable of Layer 2 transport and set to Interface Type HA.
- Select VR Sync to force synchronization of all virtual routers configured on the HA peers. Select when the virtual router is not configured for dynamic routing protocols. Both peers must be connected to the same next-hop router through a switched network and must use static routing only.
- Select QoS Sync to synchronize the QoS profile selection on all physical interfaces. Select when both peers have similar link speeds and require the same QoS profiles on all physical interfaces. This setting affects the synchronization of QoS settings on the Network tab. QoS policy is synchronized regardless of this setting.
- (Optional) Modify the Tentative Hold time.
- In , edit Packet Forwarding.
- For Tentative Hold Time (sec), enter the number of seconds that a firewall stays in Tentativestate after it fails (range is 10-600, default is 60).
- Configure Session Owner and Session Setup .
- In , edit Packet Forwarding.
- For Session Owner Selection, select one of the following:
- First Packet—The firewall that receives the first packet of a new session is the session owner (recommended setting). This setting minimizes traffic across HA3 and load shares traffic across peers.
- Primary Device—The firewall that is in active-primary state is the session owner.
- For Session Setup, select one of the following:
- IP Modulo— Distributes session setup load based on parity of the source IP address.
- Primary Device—The active-primary firewall sets up all sessions.
- First Packet—The firewall that receives the first packet of a new session performs session setup (recommended setting).Start with First Packet for Session Owner and Session Setup, and then based on load distribution, you can change to one of the other options.
- IP Hash—The firewall uses a hash of either the source IP address or a combination of the source and destination IP addresses to distribute session setup responsibilities.
- Click OK.
- Configure an HA virtual address.You need a virtual address to use a Floating IP Address and Virtual MAC Address or ARP Load-Sharing.
- In , Add a Virtual Address.
- Enter or select an Interface.
- Select the IPv4 or IPv6 tab and click Add.
- Enter an IPv4 Address or IPv6 Address.
- For Type:
- Select Floating to configure the virtual IP address to be a floating IP address.
- Select ARP Load Sharing to configure the virtual IP address to be a shared IP address and skip to Configure ARP Load-Sharing.
- Configure the floating IP address.
- Do not select Floating IP bound to the Active-Primary device unless you want the active/active HA pair to behave like an active/passive HA pair.
- For Device 0 Priority and Device 1 Priority, enter a priority for the firewall configured with Device ID 0 and Device ID 1, respectively. The relative priorities determine which peer owns the floating IP address you just configured (range is 0-255). The firewall with the lowest priority value (highest priority) owns the floating IP address.
- Select Failover address if link state is down to cause the firewall to use the failover address when the link state on the interface is down.
- Click OK.
- Configure ARP Load-Sharing .The device selection algorithm determines which HA firewall responds to the ARP requests to provide load sharing.
- For Device Selection Algorithm, select one of the following:
- IP Modulo—The firewall that will respond to ARP requests is based on the parity of the ARP requester's IP address.
- IP Hash—The firewall that will respond to ARP requests is based on a hash of the ARP requester's IP address.
- Click OK.
- For Device Selection Algorithm, select one of the following:
- Enable jumbo frames on firewalls other than PA-7000 Series firewalls.Switch ports that connect the HA3 link must support jumbo frames to handle the overhead associated with the MAC-in-MAC encapsulation on the HA3 link.The jumbo frame packet size on the firewall must match the setting on the switch.
- Select .
- In the Session Settings section, select Enable Jumbo Frames.
- Click OK.
- Repeat on any intermediary networking devices.
- Define HA Failover Conditions .
- Commit the configuration.
- Reboot the firewall after changing the jumbo frame configuration.
- Select .
- Click Reboot Device.









No comments:
Post a Comment